Nitinol Medical Devices: Revolutionizing Healthcare
 |
| Nitinol Medical Devices |
Introduction
Nitinol, an unusual alloy of nickel and titanium that shows properties of shape
memory and superelasticity, has found widespread applications in the medical
field and is transforming healthcare. Nitinol's unique properties allow it to
be designed into minimally invasive medical devices that can navigate the human
body in remarkable ways.
What is Nitinol?
Nitinol refers to the nickel titanium alloy commonly referred to by its acronym
- NiTi. When NiTi reaches its transformation temperature, it undergoes a
crystal structure change which allows it to revert to a preformed shape. This
phenomenon is called shape memory. Additionally, NiTi displays superelasticity
or pseudoelasticity, where it can withstand high amounts of strain and still
revert to its original undeformed shape upon unloading. These properties make
Nitinol light, flexible and able to be designed into intricate small diameter
medical devices.
Applications in Cardiology
Cardiology has seen some of the most revolutionary applications of Nitinol
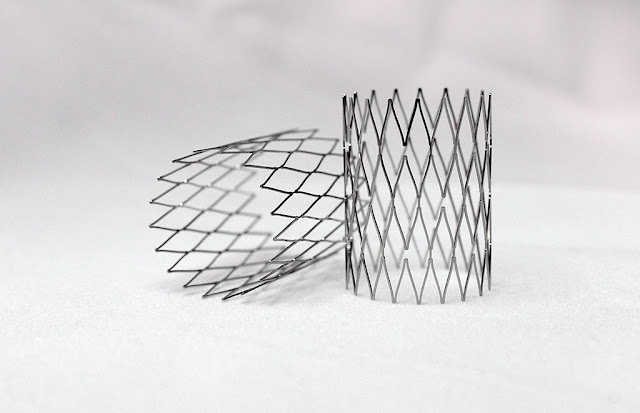
Medical Devices. Stents, which are small mesh tubes used to open
blocked arteries, were some of the earliest medical applications of Nitinol.
Nitinol stents are self-expanding - when deployed in a blocked artery, their
shape memory allows them to expand and press against the vessel wall to hold it
open. This makes insertion and placement much simpler than earlier balloon
expandable stents. Today, Nitinol stents are the standard of care worldwide for
treating coronary and peripheral artery disease.
Another major application is filter devices to capture blood clots in the heart
before they can travel to the brain and cause a stroke. Inferior vena cava
(IVC) filters made of Nitinol are deployed in the large vein leading to the
heart to trap thrombi. Their self-expanding superelastic mesh design allows
them to securely anchor in place and function for years. Retrievable IVC
filters have also been developed which can be easily removed once the risk of
clot passes, using Nitinol's shape memory.
Neurovascular Applications
In the neurovasculature - the delicate blood vessels of the brain, Nitinol has
enabled groundbreaking new procedures. Its flexibility and shape memory allows
creation of self-expanding stents much smaller than previous designs to access
vessels as small as 2mm in diameter. These neurovascular stents help treat
aneurysms - weak bulging areas in arterial walls at risk of rupture.
Coiling technologies use platinum coils delivered through a microcatheter to
fill an aneurysm, promoting clotting off from circulation. Newer flow diverter
stents constructed of Nitinol are changing the game. These ultra-flexible
stents are deployed across the neck of an aneurysm, diverting blood flow away
from it and promoting faster, more complete healing. They have vastly superior
outcomes to coiling for large and giant aneurysms.
As stroke remains a leading cause of death worldwide, continues expansion of
neuroendovascular techniques presents hope. And it would not be possible
without the enabling properties of Nitinol.
Sub-Sections and Sub-headings
Nitinol in Orthopedics
Joint replacement has traditionally relied on metal alloys like titanium and
cobalt-chrome. However, Nitinol is showing promise for next generation
implants. Its shape memory and superelasticity allows construction of
self-expanding components that can conform to complex joint geometries better
than static designs. Early research involves spinal fusion cages and total disc
replacements that deploy via Nitinol's memory effect to properly space and
support vertebral bodies. If long term testing proves successful, these passive
conforming implants could greatly simplify surgery and recovery time.
Nitinol in Urology and Gastroenterology
Two areas seeing extensive use of Nitinol are urology and gastroenterology due
to demands of navigating convoluted anatomies. Ureteral stents made of Nitinol
self-guide from the kidney to the bladder, releasing its memory effect shape
change once in proper position to drain urine. Similarly, esophageal stents
allow eating and drinking by bracing open collapsed areas of the swallowing
tube.
Retrievable biliary and pancreatic stents that help drain blockages of the
liver and pancreas ducts over months would not be possible without Nitinol. Its
shape memory and flexibility permit easy removal after therapy, instead of
requiring a second surgery. Nitinol is also used for sutures, surgical meshes
and staples in pelvic organ prolapse and hernia repair where superelasticity
eases tissue handling.
Nitinol in Vascular Surgery
With Nitinol stents revolutionizing cardiology and neurovascular care, it was
only a matter of time before orthopedic extremities work utilized shape memory
technology. Nitinol self-expanding stents show promise to restore blood flow in
advanced cases of peripheral arterial disease affecting lower limb circulation.
Their flexible scaffolding can navigate tortuous superficial femoral and tibial
arteries to open blockages where traditional balloon angioplasty and bare-metal
stents have failed.
Other areas include aortic endografts for abdominal aortic aneurysm repair
which rely on Nitinol superelastic frame and stent designs to conform to
complex 3D anatomies of the aorta and iliac arteries. New retrievable formats
also allow less invasive alternatives if future open surgery becomes necessary.
With lifestyle limiting claudication on the rise, shape memory alloys offer new
hope.
From simpleNitinol stents and filters to complex flow diverters, retrievable
implants and next generation joint designs, shape memory technology is
revolutionizing minimally invasive surgery. Millions of lives have already
benefited from these novel applications with more on the horizon. As material
property insights continue advancing, new frontiers in orthopedics, urology,
vascular and even wider surgical specialties await. Ultimately, it is Nitinol's
versatility that makes it so well suited to medical environments and drives
ongoing innovation improving patient care worldwide.
Get
more insights on this topic: Nitinol
Medical Devices


Comments
Post a Comment