The Next Frontier in Transportation: Robotaxis and Beyond
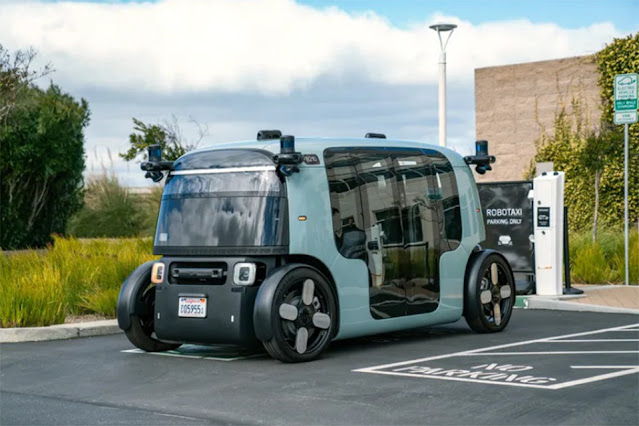

Robotaxis The transportation industry is on the verge of a major revolution thanks to the emergence of robotaxis. Robotaxis, which are self-driving taxis without a human driver behind the wheel, have the potential to drastically change how we get around our cities. With major tech companies pouring billions into robotaxi development, it seems this new mode of transportation is just around the corner. What is a Robotaxi? A robotaxi, sometimes called a driverless taxi or autonomous taxi, is essentially an automated vehicle designed to provide on-demand, point-to-point transportation for paying customers on public roads. The key features that define a robotaxi are: - No human driver inside the vehicle - Robotaxi s are fully autonomous vehicles capable of navigating roads and transporting passengers without a human operator behind the wheel. Advanced sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence allow the vehicle to drive itself. - On-demand service - Customers can hail and pay for rid