Empowering Healthcare Worldwide: Understanding Global Manual Resuscitators
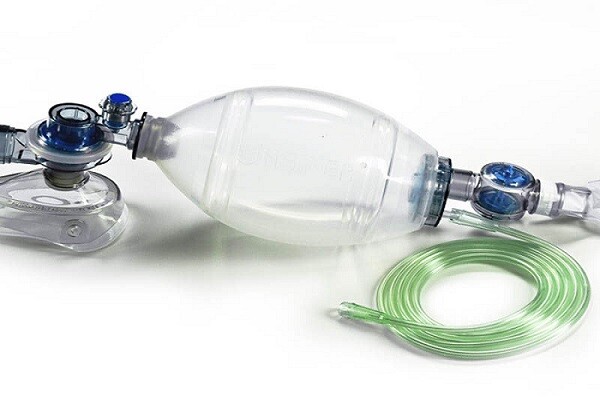 |
| Global Manual Resuscitators |
Manual resuscitators, commonly known as bag-valve-mask (BVM)
devices, are designed to provide manual ventilation to patients who are not
breathing adequately or at all. Comprising a self-inflating bag, a one-way
valve, and a face mask, these devices allow healthcare providers to manually
deliver oxygen to the lungs, ensuring vital oxygenation and ventilation.
One of the most significant aspects of manual resuscitators
is their versatility. They can be used across various healthcare settings,
including hospitals, ambulances, clinics, and even makeshift medical facilities
in remote or resource-limited areas. This adaptability makes them indispensable
in both developed and developing regions, where access to advanced medical
equipment may be limited.
Moreover, manual resuscitators are not only essential in
emergency situations but also play a crucial role in routine patient care. They
are often utilized during anesthesia induction, post-operative recovery, and in
scenarios where mechanical ventilation is not readily available or feasible.
This underscores their significance as a fundamental tool in the armamentarium
of healthcare providers worldwide.
In recent years, advancements in manual resuscitator
technology have further enhanced their efficacy and usability. Innovations such
as ergonomic designs, integrated pressure gauges, and enhanced mask seals have
improved user experience and patient outcomes. Additionally, the development of
disposable components has simplified maintenance and reduced the risk of
cross-contamination, addressing concerns related to infection control.
The global landscape of manual resuscitators reflects a
dynamic interplay of factors, including technological innovation, regulatory
standards, and healthcare infrastructure. While high-income countries often
boast advanced medical systems with access to cutting-edge equipment, many low
and middle-income countries face challenges in procuring essential medical
devices, including manual resuscitators.
Addressing these disparities requires a concerted effort
from various stakeholders, including governments, non-profit organizations, and
the private sector. Initiatives aimed at improving access to essential medical
equipment, along with capacity-building programs for healthcare providers, can
help bridge the gap and ensure equitable distribution of lifesaving tools like
manual resuscitators.
Furthermore, education and training play a pivotal role in
maximizing the potential of manual resuscitators. Healthcare providers must
receive comprehensive training on proper usage, maintenance, and
troubleshooting of these devices to ensure safe and effective patient care.
Simulation-based training programs offer a valuable opportunity for hands-on
practice and skill development, empowering clinicians to confidently handle
emergency situations.
As we navigate the complexities of the global healthcare
landscape, it is imperative to recognize the indispensable role of manual
resuscitators in saving lives and alleviating suffering. These humble yet
powerful devices embody the spirit of empowerment, enabling healthcare
providers worldwide to deliver timely and effective care, regardless of geographic
location or resource constraints.

Comments
Post a Comment