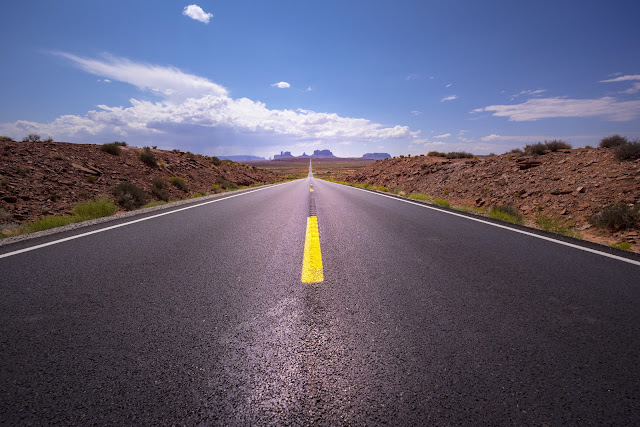
Asphalt: An Essential Building Material
 |
| Asphalt |
Asphalt is one of the most widely used construction
materials in the world. With its ability to pave roads, construct highways,
roof structures and more, asphalt plays a vital role in building infrastructure
globally.
What is Asphalt?
Asphalt is a sticky, black and highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of
petroleum. It is a byproduct of the oil refining process in which crude oil is
separated into various petroleum products. Asphalt consists of predominantly
saturated aliphatic and cycloaliphatic hydrocarbons mixed with aromatics and
resins. When processed and mixed appropriately, it transforms into a versatile
construction material.
Composition and Production
The key components of Asphalt
are bitumen (also known as asphalt cement) and aggregates like sand, gravel or
crushed stone. Bitumen is a hydrocarbon pitch that acts as a binder to hold
aggregate particles together. For production, bitumen extracted from crude oil
refining is heated and mixed with aggregates at high temperatures. This results
in a homogeneous and workable blend that hardens upon cooling. Different
aggregate gradations and bitumen contents can be adjusted based on the intended
use.
Uses of Asphalt
Road Construction
Asphalt pavement is the most common road surfacing material due to its high
durability, flexibility and cost-effectiveness. It provides a seamless,
waterproof surface that can withstand the pounding of millions of vehicle tires
passing over it each year. Asphalt roads are sustainable, requiring less maintenance
compared to other road surfaces.
Roofing
Rolled asphalt or asphalt shingles are used extensively in commercial and
residential roofing for their waterproofing ability. A fibreglass or felt mat
embedded with asphalt forms shingles that offer roof protection against sun,
rain and snow.
Other Construction Uses
Asphalt is also used in bridge deck waterproofing, sound barriers, parking lots
and playgrounds. It is an integral material in hydraulic structures such as
dams and canals due to its ability to withstand constant water exposure.
Asphalt-based glues and adhesives are common industrial and do-it-yourself
products as well.
Advantages of Asphalt
Cost-Effective Solution
The cost of asphalt pavement per mile is relatively low compared to concrete or
brick roads, making it an affordable choice for highways, streets and
driveways. Its use results in significant cost savings for construction
projects.
Eco-friendly Material
Since asphalt is a byproduct of oil refining, its production does not involve
extracting additional raw materials. It is 100% recyclable at the end of its
service life, reducing environmental impact. Asphalt roads require little
maintenance and have a long lifespan of over 20 years.
Durability
Asphalt pavements last longer than other surfacing options if designed and
constructed properly. Its elastic nature allows it to flex without major damage
from regular traffic use and climate changes. Asphalt pavements remain smooth
and pothole-free for years with only minor repairs needed.
Easy to Install and Repair
Asphalt is laid quickly on-site with specialized pavers and compacting
equipment. Partial or full-depth repairs can also be executed rapidly without
much disturbance. This improves construction efficiency and reduces traffic
disruptions.
Challenges with Asphalt
Despite its widespread popularity, asphalt does present a few limitations:
Vulnerability to Fuel Spills
Fuel spills from vehicles can cause asphalt to soften and damage its structure
prematurely. Proper drainage systems are required to prevent such occurrences.
Rutting from Heavy Traffic
Under extreme heavy loading, continual flexing of asphalt over time may lead to
surface depressions called ruts. This necessitates more frequent repairs on
heavily-travelled roads.
Reflective Heat Absorption
Black asphalt surfaces absorb large amounts of sun heat, causing the road
surface temperature to increase substantially on hot summer days. This
exacerbates the urban heat island effect. Light-coloured pavements are now used
in some areas to mitigate this.
Asphalt has evolved into one of humanity's most important construction
materials, enabling large-scale infrastructure development across the globe.
With continued technological improvements and sustainability efforts, asphalt
promises to remain the premiere paving solution well into the future. Its
unique mix of qualities like affordability, durability and versatility have
made it the material of choice for roadways, structures and more.
For
more details on the report, Read- https://www.trendingwebwire.com/asphalt-growth-demand-and-overview/


Comments
Post a Comment